
Inventory is classified as a current asset and will show up as such on the business’s balance sheet. Accounting and inventory, while both critical components of any business, may seem like two separate tasks, but they are very much linked. Calculating your inventory, or inventory accounting, is a key part of a business’s success. Methods to value the inventory include last-in, first-out, first-in, first-out, and the weighted average method. For some businesses — such as retailers of holiday items — seasonal stock adjustments can also be a smart idea. It involves discontinuing, consolidating, or discounting slow-moving inventory to free up space for fast-selling items, or potentially even throwing out or donating unsellable stock.
What is the Weighted Average Costing Method?
The subsequent depreciation of the cost is included in production overheads in future periods over the asset’s estimated remaining useful life. While the majority of US GAAP companies choose FIFO or weighted average for measuring their inventory, some use LIFO for tax reasons. Companies using LIFO often disclose information using another cost formula; such disclosure reflects the actual flow of goods through inventory for the benefit of investors. The perpetual inventory system is a highly sophisticated system that keeps tracks of goods as they are purchased and sold in real time using a bar code scanner and computer system. For instance, a sandwich shop’s delivery truck is not considered inventory because it has nothing to do with the primary business of making and selling sandwiches. To a car dealership, on the other hand, this truck would be considered inventory because they are in the business of selling vehicles.
Inventory Formula
Many business owners will use accounting software to help them track and calculate financial information, including inventory management and accounting. Millions of individuals and businesses manage inventory using QuickBooks as a means to simplify this monumental undertaking. That means keeping accurate and up-to-date financial records for business management purposes and tax return filing. By following International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), a business can determine the appropriate information as required, like corresponding inventory accounting numbers. Company management, analysts, and investors can use a company’s inventory turnover to determine how many times it sells its products over a certain period of time. Inventory turnover can indicate whether a company has too much or too little inventory on hand.
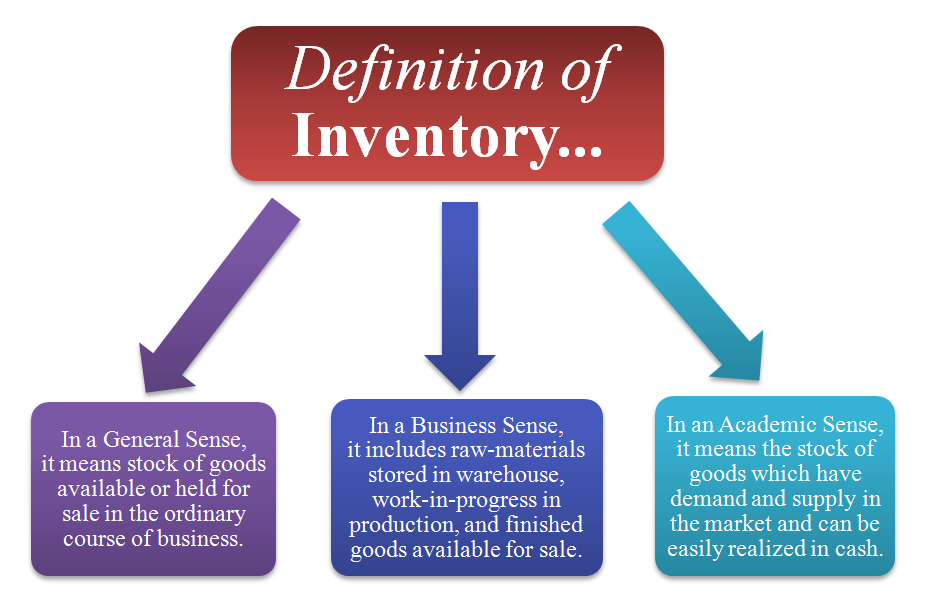
How Do You Define Inventory?
In practice, for an acquired business this often requires rapid realignment to its new parent’s group methodologies and systems. In general, US GAAP does not permit recognizing provisions for onerous contracts unless required by the specific recognition and measurement requirements of the relevant standard. However, if a company commits to purchase inventory in the ordinary course of business at a specified price and in a specified time period, any loss is recognized, just like IFRS Standards.
On the income statement, the cost of goods sold (COGS) is deducted from revenue to determine gross profit. Methods that assign higher costs to COGS, like LIFO during inflation, can decrease gross profit, while methods like FIFO can increase it by assigning lower costs. These variations can impact profitability ratios and, consequently, the perception of financial performance by investors and analysts. All businesses must report their inventory to their country’s revenue collection agency.
- Namely, inventory accounting allows businesses to assess where they may be able to increase profit margins on a product at a particular place in that product’s cycle.
- In accounting, inventory consists of items at different production stages and assets for your business.
- For instance, a sandwich shop’s delivery truck is not considered inventory because it has nothing to do with the primary business of making and selling sandwiches.
With careful consideration and implementation of inventory accounting strategies, businesses can effectively manage their inventory assets and drive success in today’s competitive market. Methods like LIFO can result in lower taxable income due to higher COGS figures, potentially reducing the tax burden. However, tax regulations and reporting requirements vary by jurisdiction, and businesses should consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance.
Effective finished goods inventory management helps your business meet customer demand, reduce storage costs, and direct supply chain efforts without too many hurdles. When poorly managed, finished goods will add problems such as stockouts, overstocking, higher carrying costs, and reduced profitability. Given ongoing supply chain troubles, skyrocketing prices, and never-ending shipping delays, eCommerce brands provision for income tax definition formula have been going through a seriously tough time. Amidst all this uncertainty, there’s one thing you can take charge of – gaining a solid understanding of your financial statements and inventory items. Inventory accounting is a critical aspect of managing a company’s inventory assets. Accurate valuation and proper accounting methods are essential for financial reporting, profit analysis, and taxation purposes.
Therefore, each company in a group can categorize its inventory and use the cost formula best suited to it. In some cases, NRV of an item of inventory, which has been written down in one period, may subsequently increase. In such circumstances, IAS 2 requires the increase in value (i.e. the reversal), capped at the original cost, to be recognized.
The operating assumptions in a financial model will be set based on the historical trends of the company’s days inventory outstanding (DIO) to guide the pro-forma forecast. Initially, the days inventory outstanding (DIO) is calculated for the trailing periods to have historical data to reference. The days inventory outstanding (DIO) formula is equal to the inventory balance divided by COGS, which is then multiplied by 365 days. In the final step, the resulting figure obtained after subtracting COGS from the beginning inventory balance is added to the value of new raw material purchases to arrive at the ending inventory balance. In accounting, inventory describes a wide array of materials used in the production of goods and the finished goods waiting to be sold.
A higher turnover ratio suggests effective inventory management and sales processes, while a lower ratio may indicate overstocking or obsolescence. This ratio can inform strategies for inventory control, procurement, and sales. The weighted average method, or average cost method, deals with inventory differently than the FIFO and LIFO methods. This method dictates that the overall value of an inventory is based on the average cost of items purchased and sold within a given accounting period. In accounting, inventory consists of items at different production stages and assets for your business. Effect inventory accounting helps businesses to efficiently create, market, and ship products.